Ultrasonic vs. Infrared Web Guide Sensors: Choosing the Right Technology for Your Applications
In the automated industries, web guide systems are crucial to ensure the accurate alignment of materials that are continuous like foil, film or fabric. In the core of these systems are web guide sensors, which are responsible for detecting the lateral direction of the web material and giving feedback to correct adjustments. One of the most widely utilized sensor technologies are infrared and ultrasonic sensors. Each one has its own advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications. This article focuses on the differences between ultrasonic and infrared web guide sensors in order to help manufacturers select the most suitable sensor solution for their needs.
What are Ultrasonic Web Guide Sensors
Ultrasonic web guide sensors are non-contact devices that are used in automated systems to determine and keep the horizontal alignment of web materials, such as plastic film, paper, foil and fabrics during the production process or during conversion. They play an essential part for web guide systems to ensure that the materials move in the right direction through the machine without misalignment, wrinkles or tracking errors.

Working Principle
Ultrasonic web guide sensor functions using ultra-high frequency sound waves. This is how they work:
- Emission: This sensor releases ultrasonic signals (typically within 20kHz and 400kHz) towards the object.
- Reflection: Sound reflections reflect off the edge or surface of web materials.
- Reception and Calculation: The sensor detects the signal reflected and determines the distance to the material, based on its time-of-flight (the amount of time it takes the signal to come back).
- Edge Detection: Through scanning the web, or with dual transducers the sensor can determine the exact location of the edge of the web.
- Feedback: This information about the position is passed to a controller that adjusts actuators to ensure an appropriate alignment of the web.
Advantages
- Non-Contact Operation: The web is not physically in contact with web is safe, thus avoiding the risk of causing damage to delicate or sensitive materials.
- Insensitive to Material Properties: Effectively detects opaque, transparent glossy, matte or printed materials, without being affected by reflectivity, color or patterns.
- Environmental Tolerance: Unaffected by ambient light, which makes them ideal for bright and dark environments.
- Durability and Low Maintenance: Less moving parts and less resistance to dirt or dust accumulation can lead to a longer service life and fewer maintenance requirements.
- Versatility: It is suitable for a variety of industries and materials such as printing, packaging, plastic film, and textiles production.
Limitations
- Sensitivity to Temperature and Air Turbulence: Performance can be affected by extreme temperature fluctuations, or with strong air currents, which could cause distortion in sound waves and their propagation.
- Limited Resolution: Although they are adequate for a variety of applications Ultrasonic sensors can offer less edge detection precision than optical sensors for high accuracy applications.
- Material Thickness and Shape Considerations: It may be a challenge with extremely thin and light materials that are unable to reflect sound, or have curved web edges that scatter sound waves unevenly.
- Speed Limitations in High-Precision Applications: In ultra-high-speed or micro-alignment procedures infrared or optical sensors may provide greater response time and more precise control.
Common Applications
The ultrasonic guide sensor is widely employed in various industries, such as:
- Packaging
- Printing
- Textiles
- Plastic film converts to
- Systems for labeling and laminating

What are Infrared Web Guide Sensors
Infrared web guiding sensors that emit infrared light are optical sensors that are used for web guiding equipment that determine the lateral position of a material that is moving that includes foil, film, paper or even textiles, during the process. These sensors play an important part in making sure that the web is straight within the manufacturing line and avoiding problems such as the misalignment of materials, waste material, or printing mistakes.
Working Principle
Infrared web guide sensors work by relying on infrared light detectors. This is how they function:
- Infrared Emission: The sensor emits an infrared beam of light, which is typically located within the infrared near spectrum.
- Refraction or Interruption: light infrared is either reflected off the surface of the web or is block by the web surface, according to the style (reflective or transmissive sensors).
- Detection: The sensor is able to detect the intensity or discontinuity of the beam infrared to determine the boundary of the internet.
- Edge Position Calculation: The difference of IR responses between background and the web is used to determine exactly where Web’s edges.
- Control Feedback: The sensor transmits the position of the edge to a controller, who adjusts actuators to correct web’s alignment as required.
Advantages
- High Precision and Fast Response: Ideal for high-speed applications in which speedy and precise edge detection is required.
- Contact-Free Measurement: There is no chance of causing damage to the web material.
- High Resolution: They are capable of detecting tiny moves or edges that are narrow They are suitable for processing narrow webs and precise tolerances.
- Compact Design: Small form factors permit installation in small spaces, and also integration into smaller system of guiding.
- Real-Time Tracking: Rapid response allows for instant correction of even the tiniest web deviations.

Limitations
- Sensitivity to Material Type: It is difficult to work with semi-transparent or transparent films that permit IR light to traverse and make the detection of edges difficult.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Performance may be impacted by ambient light, dust or reflective surfaces that can affect IR signals.
- Material Reflectivity Dependence: Materials that are highly reflective or glossy could cause inconsistent readings because of uneven light reflection.
- Maintenance Requirements: Optics components can require periodic cleaning to ensure their accuracy particularly in dirty or dusty industrial environments.
Typical Applications
Infrared web guide sensors are used extensively in:
- High-speed labeling and printing equipment
- Converting narrow webs
- Packaging lines
- Textile edge tracking
- Coating and laminating processes
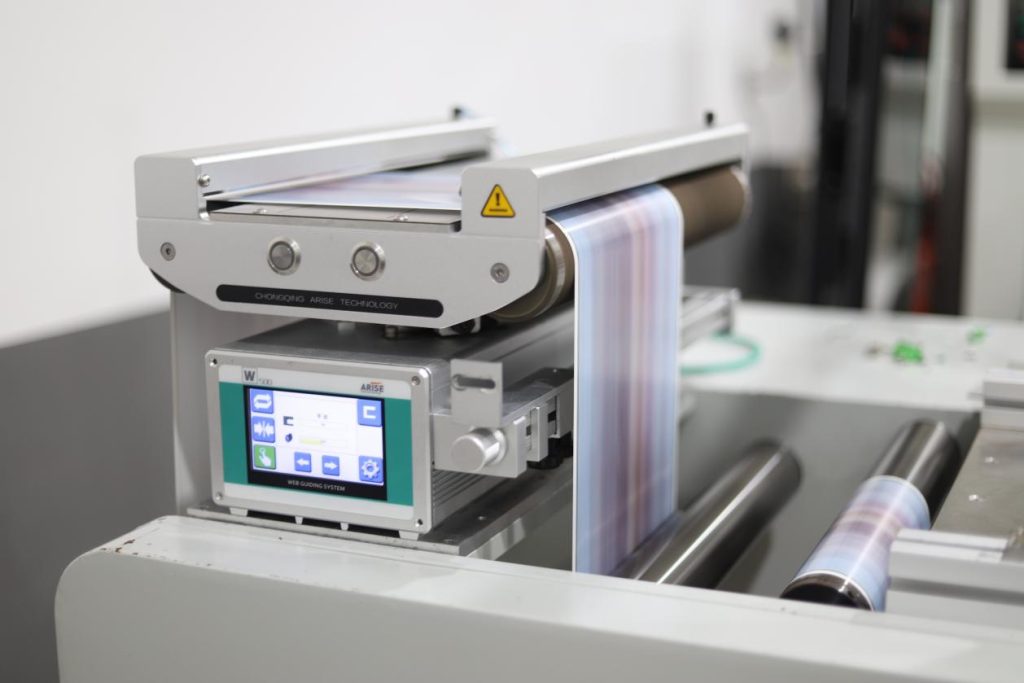

Comparative Analyses of Ultrasonic as compared to. the Infrared Guide Web Sensors
| Feature | Ultrasonic Web Guide Sensors | Infrared Web Guide Sensors |
| Detection Method | High-frequency reflection of sound waves | Infrared light reflections or interruption |
| Material Compatibility | Ideal for opaque, transparent or printed materials. | Only with reflective materials. |
| Environmental Sensitivity | More unaffected by ambient light, dust or the conditions of the surface. | Sensitive to light, dust and reflection of the material |
| Response Time | Moderate | Fast |
| Accuracy & Resolution | Ideal for use in general | High quality, ideal in narrow edge detection |
| Maintenance Requirements | Very low; frequent cleaning required | Moderate. The optical lens could require periodic cleaning |
| Best For | Films, foils, paper, textiles in variable conditions | Opaque matte materials that are used in well-maintained, controlled conditions. |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to high |
| Installation Flexibility | Typically, they are larger because of the sound wave spacing | Easy to install and compact in tight space |
| Sensitivity to Material Surface | Unaffected by color of the surface or gloss | Infected by uneven or shiny surfaces |
| Performance of Thin Materials | Could be inconsistent with thin or reflective surfaces | It is effective with light but transparent materials. |
Key Considerations for Choosing Between Ultrasonic and Infrared Web Guide Sensors
1. Understanding Material Characteristics
The most important aspect to consider is the nature of web materials. Ultrasonic sensors utilize sound waves to identify edges in the material. They are not affected by visual properties. This makes them suitable for transparent films and multi-colored surfaces. They are also ideal for printed webs or any other material with different textures. In contrast, infrared sensor are based on the detection of differences in the infrared light reflectivity as well as transmission. That restricts their efficacy when used with clear or reflective materials. If the material used for web is shiny or transparent ultrasonic sensors are generally the best choice.
2. Environmental Suitability
The environment in which the sensor operates greatly affects the sensor’s performance. Ultrasonic sensors are extremely resistant to the most challenging conditions. They are not affected by light from the outside and retain the same level of performance in even humid conditions. This makes them ideal for harsh industrial environments where environmental control is very limited. Infrared sensors on the contrary, are most effective in controlled and clean conditions. The accumulation of dust, the high intensity of light or reflective components of machines can hinder the infrared detection process which could lead to an error in alignment.
3. Precision and Speed Requirements
For applications that require rapid response times and high-resolution edge tracking, such as narrow-web printing or high-speed printing, infrared sensors typically offer a competitive edge. Their speedy processing of data allows for precise accurate, real-time corrections. Although ultrasonic sensors provide sufficient accuracy for many applications, they might not react as fast to sudden changes in the web, particularly in situations where millimeter-level adjustments are crucial.

4. Maintenance and Reliability
The maintenance of web guide sensors and the durability over time are crucial aspects to consider. Ultrasonic sensors, which have less sensitive optical components typically need less care and more resistant to performance decline due to dust or dirt. Infrared sensors are comprised of emitters and lenses that may build up dust or smudges over time, which can affect their ability to recognize the web with precision. In facilities that require uptime and maintenance access is not always available the use of ultrasonic sensors is more suitable.
5. Installation Space and System Integration
The flexibility of installation is essential, especially for machines with small layouts. Infrared sensors tend to be smaller and simpler to fit into small space. Their tiny size and light design makes them ideal for machines in which space is limited. Ultrasonic sensors, dependent on the range of sensing and beam size, may require additional space for positioning and alignment, which can be a problem in tight space conditions.
6. Cost vs. Application Needs
While both sensors are priced reasonably however, infrared sensors can have a higher price due to their high-precision electronics and optics. However, the choice should not be solely based on the upfront costs. Instead, it is important to be by evaluating the reliability of performance as well as materials compatibility, maintenance efforts and efficiency of the process. In some instances it is worth investing in a more expensive sensor that is more closely with the application could yield significant savings due to less downtime and reduced waste.

Final Thoughts
Ultrasonic and infrared web guide sensors provide reliable solutions for ensuring alignment of the web in automated systems. However, their efficiency is dependent on the type of material used and the environment. Ultrasonic sensors offer robust performance in a wide range of conditions, while infrared sensors provide superior precision when operating in controlled conditions. Understanding these differences allows engineers and operators customize their web guide systems to achieve the optimal performance and minimized downtime.
For maximum efficiency, advanced web guiding control systems integrate two technologies to leverage both strengths. As technology advances, the hybrid and intelligent sensor solutions could become the future of precise web guiding.

