Laser-based vs. Camera-based Web Guide Systems: Which Technology to Choose
Web guide systems align the web consistently, preventing misalignment, which can cause defects, waste and downtime. Laser-based and cameras-based systems are two of the most commonly used technologies for web guiding. Each system has its own advantages, limitations and ideal applications. Understanding the differences between laser-based and camera-based web guide systems can help manufacturers choose the most appropriate technology for their production requirements.

Table of Contents
Understanding Laser-based Web Guide Systems
Laser-based web guide systems use a laser emitter and receiver to detect the position. The web guiding sensor measures the reflection of a laser beam that is aimed at the web. The laser reflection changes when the web moves away from the centerline. This causes the system to adjust the guide rollers and other parts automatically to realign it.

Advantages
- High Accuracy and Precision: Laser-based systems offer accuracy to fractions millimeters. These systems are perfect for applications that require precise alignment of the web, such as high-speed printing and coating.
- Faster Response Time: Laser sensors are able to detect misalignments in a matter of seconds. They are ideal for fast-moving production lines, where they can be used to make real-time adjustments in order to maintain alignment.
- Non-contact Measurement: Lasers don’t touch the material, so there is less wear on the system. The non-contact operation leads to less maintenance and a longer system life than contact-based technologies.
- Low Environmental Sensitivity: Laser-based web guiding systems can operate effectively in dusty or dirty environments. Laser detection can be affected by extreme conditions such as heavy fog or mist. However, in the majority of industrial settings, these systems are able to perform well.
- Low Maintenance Requirements: With fewer moving components, laser-based systems for web guidance are relatively simple to maintain. Lack of physical contact between sensor and web reduces the risk of damage over time.
- Easy Installation and Operation: Laser web guide systems are easier to install and use than more complex camera systems. For basic web tracking, they require fewer parts and don’t need to be programmed or calibrated.
Limitations
- Environmental Sensitivity: Laser-based web guide systems can be affected by extreme conditions, even though they are resistant to dirt and dust. Dirt, moisture, and fog can cause the laser to scatter, resulting in incorrect readings. In these environments, regular cleaning and maintenance is required.
- Material Limitations: Laser systems have difficulty with materials that are transparent, highly reflective or irregularly shaped. Materials like mirrors, clear films or shiny metals can reflect the laser in unpredictable ways. This makes accurate alignment difficult.
- Limited Functionality: Laser-based web guiding systems are designed to track the position of webs. They are not as equipped to detect defects, printed patterns or textures. A camera-based system may be the better choice if your application needs to track additional features (such as textures or printed graphics) on the web.
- Alignment and Calibration: While laser web guides require less maintenance than other laser systems, they do need periodic calibration in order to ensure the laser is aligned correctly and working within parameters. A laser that is not aligned correctly can result in inaccurate measurements and poor performance.
- Cost Considerations: While laser-based systems can be cost-effective due to their precision and performance, there are costs associated with the replacement of damaged laser components or upgrading a system for more complicated tasks.
Common Applications
- Printing Industry: Ensure proper alignment of film or paper rolls during printing processes in order to avoid misalignment.
- Laminating and Coating: Aligning the webs on laminating & coating machines where precision is essential for consistent product quality.
- Textile Industry: Guide textile webs through equipment to ensure uniformity in weaving, knitting or finishing.
- Film and Foil Manufacturing: Ensure that plastic films and aluminum foils are aligned throughout the extrusion and other processes.
- Packaging Industry: Guide packaging materials such as labels, flexible film, and cartons on packaging lines.

Understanding Camera-based Web Guide Systems
Camera-based web guide systems track the web position using cameras. They are usually CCD image sensors or CMOS image senors. These cameras take images of the web, and then process the data in order to determine the alignment. The software detects edges, patterns, or features of the web, such as printed marks, and provides feedback for the system to adjust accordingly.

Advantages
- Versatility of Material Handling: Camera-based systems are excellent at handling materials with irregular shapes or textures, as well as those with complex patterns. Camera-based systems are more flexible than laser-based ones, which rely on uniformity. They can adapt to materials with irregular shapes, patterns, and textures.
- Multi–feature Detection: Camera-based web guiding systems can track multiple web features. They can detect, for example, printed logos and barcodes as well as edges, color variations, or even edge variations. The ability to track other features is crucial in industries such as printing, packaging and textile manufacturing.
- High Flexibility: Camera-based system are adaptable to a variety of web materials, production environments and other factors. They can detect wrinkles, defects and other visual differences in both transparent and opaque materials.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Camera-based systems are capable of guiding webs and also serving as tools for quality control. The system, by tracking certain features, can identify printing mistakes, defects or deviations in design or color, which can then be corrected in real time, reducing waste and rework.
- Real-time Adjustment: The ability to detect misalignment and react in real time of camera-based web guiding system allows for quick corrections. This reduces downtime, and improves overall production efficiency. Continuous monitoring allows for the detection of even the slightest shifts within the web, ensuring high quality standards during the entire manufacturing process.
- Improved Performance with Complex Applications: Camera-based systems are especially advantageous when aligning the web with regard to printed marks, patterns or other visual indicators which are crucial to the quality of the final product.

Limitations
- Higher Initial Cost: Camera-based systems are typically more expensive than laser-based systems. Initial investment can be higher due to the cost of cameras, image-processing software and associated hardware, such as lighting systems. This can be an issue for companies that have a tight budget or do not need the extra features provided by camera-based systems.
- Slow Response Time: While camera-based web guide systems can be accurate, their processing is typically more complex than that of laser systems. A slight delay can be introduced by the need to capture images, process them, and analyze them, particularly at high production rates. This delay can be problematic in applications that require ultra-fast responses (e.g. printing at high speeds).
- Environmental Sensitivity: Camera-based systems are more sensitive to conditions like dirt, dust and moisture. The web guiding performance can be affected if the lenses are dirty or obstructed. Cleaning and maintaining the cameras is required, increasing operational costs and downtime.
- Complexity of Setup and Calibration: Setup can be time-consuming due to the need for precise placement of cameras, lighting control and alignment software. The system may also need periodic calibration, particularly if production conditions or materials change.
- Maintenance Requirements: The camera lenses and sensors may accumulate dust and dirt. This can cause a distorted view and inaccurate measurements. To keep the system working optimally, regular maintenance is required, including cleaning and calibration. Camera-based systems require more maintenance than laser-based ones.
- Lighting Dependence: The performance and effectiveness of camera-based web guiding systems based on cameras can be affected by lighting conditions. Image recognition accuracy can be affected by uneven lighting or ambient light changes. Proper lighting maintenance and setup is essential to achieving optimal performance.
Applications
- Printing Industry: Tracking patterns, logos and color accuracy in high-speed printing to ensure proper alignment of material.
- Packaging: Guide and align flexible packaging materials, such as printed film, labels, or pouches, to ensure the print design is aligned with the packaging elements.
- Textile Industry: Monitoring and alignment of woven or knitted fabric, which has a variety of textures or patterns.
- Film and Foil Production: Manage complex webs of plastic film and foils with intricate markings and coatings.
- Converting: Ensures precise alignment when converting paper, cardboard and other materials. This may include multiple layers with printed content.

Key Differences between Laser-based and Camera-based Web Guide Systems
| Feature | Laser-based Web Guide Systems | Camera-based Web Guide Systems |
| Precision | Ideal for high-speed applications. | Image processing may result in a slightly slower response time, despite the high precision. |
| Response time | Real-time detection, adjustment and monitoring. | Due to the processing of images, it is slightly slower. |
| Material Flexible | It is best for uniform material, but may not work well with reflective or translucent webs. | Ideal for materials with complex patterns, textures or irregular shapes. |
| Feature Detection | Primarily detects the web position and alignment. | Can detect multiple features, such as logos, edges and colors. |
| Cost | Costs are generally lower due to the simpler technology and fewer parts. | Initial cost is higher due to the cameras, image processing software, and hardware. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Minimal moving parts, low maintenance. | Maintenance is required, including cleaning and calibration of the lenses. |
| Installation | Installation and setup is simple. | Installation and setup is more complex, requiring the proper placement of cameras and lighting control. |
| Environmental Sensitivity | They are less sensitive to dust and dirt, but they can still be affected by extreme weather conditions. | The sensitivity to dust, dirt and lighting is a requirement for regular cleaning. |
| Lighting Dependency | No effect on lighting conditions | Image recognition is dependent on the proper lighting configuration. |
| Versatility | Handling non-uniform material is less versatile. | Highly versatile web material with different patterns, textures and colors. |
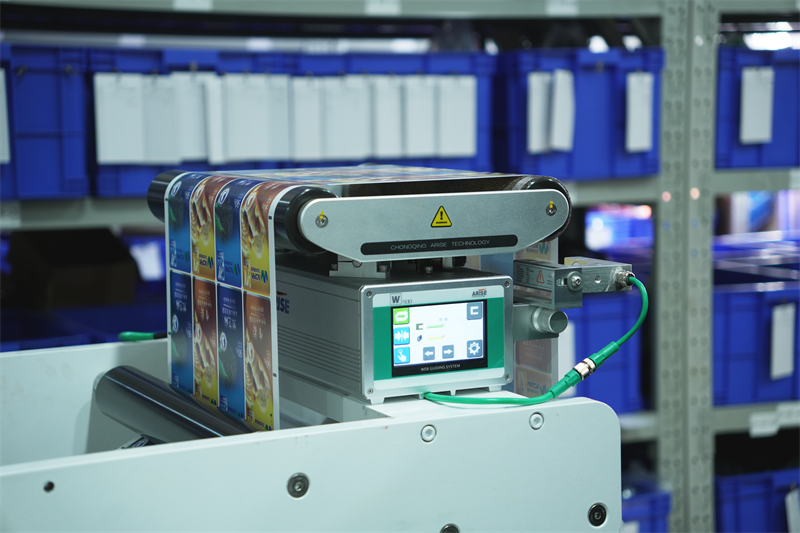

Key Factors to Consider for Choosing Between Laser-based and Camera-based Web Guide Systems
There are several factors that you should consider when choosing between camera-based and laser-based web guide systems ,which can have a significant impact on the accuracy, efficiency and cost-effectiveness your production process. Understanding these factors will help you choose the best suited web guiding control systems for your specific application.

1. Precision and Speed Requirements
In high-speed production environments, where the alignment of webs must be continuously monitored, precision and response times are essential. Laser-based systems are ideal for applications requiring rapid corrections such as high-speed coating or printing processes. Camera-based systems are still very accurate but may have a slight delay because of the image capture and process involved. This is important in environments where milliseconds are crucial.
2. Material Types and Complexity
The type of material used in the web is crucial to determining which system will be most effective. Laser-based web guide systems work best with simple materials that are uniform, like paper or clear plastic film. They may have difficulty with materials that are highly reflective or transparent, as they can interfere with laser beams. Camera-based web guide systems, on the other hand are much more versatile. They can work with a wide range of materials, including those that have complex textures, patterns or printed designs. Camera-based systems are more flexible in industries such as packaging, where barcodes and logos must be precisely aligned.
3. Application Complexity
Another important factor is the complexity of the application. A laser-based system may be the most suitable option if your main goal is to maintain a simple web alignment. This will save you time, money, and effort. If you want to monitor more than just the position of the web, but also other features such as logos, defects or print marks, then a camera-based solution is better suited. Camera-based systems can detect and adjust to multiple features at once, which is crucial for applications like printing, textiles and packaging, where web alignment and other quality control factors need to be tracked.
4. Cost Considerations
The cost is always an important factor in choosing industrial equipment. Laser web guide systems are more cost-effective both for the initial investment as well as ongoing maintenance. Costs are lower due to the simpler technology, less components and easier setup. Camera-based systems require a larger upfront investment because of the cameras, image processing equipment, and specialized computer software. Camera web guide systems also tend to require more maintenance due to their need for cleaning and calibration. You should weigh the higher price of a camera system against the added capabilities to see if it aligns with the production goals.
5. Maintenance and Reliability
For minimizing downtime, and to ensure consistent production, it is essential to consider the maintenance requirements and reliability of the web guide system. Laser-based systems require little maintenance, have few moving parts, and are less likely to malfunction. They tend to last longer as they don’t have physical contact with the internet. Camera-based systems require frequent maintenance, despite their reliability. Lenses must be cleaned frequently, and image processing software can need to be updated to meet new production requirements. If minimal downtime is a concern, and ease of maintenance is a consideration, then a laser-based solution may be the best option.
6. Environmental and Space Constraints
Both laser-based and camera systems are affected by environmental factors. Laser-based systems, provided they do not exceed extreme environmental conditions like dust or humidity are less susceptible to these factors. They are therefore a good option for harsher industrial settings where maintaining cleanliness is not always possible. Camera-based systems are sensitive to dust, dirt and poor lighting, which can block the lens or interfere with image recognition. Laser-based systems are also more compact and can be easily integrated into production lines with limited space.
7. Flexibility
Flexible web guiding systems are important for manufacturers that anticipate future changes in materials used or upgrades to production lines. Camera-based systems are more versatile, since they can be adapted to different materials and used for web guiding as well as quality inspection. A camera-based web guiding system may be more suitable for the future if your production processes will evolve in the near future or you plan to use a variety of different materials. Laser-based web guide systems are effective in certain applications but less adaptable when it comes to changing web material complexity and new production requirements.

8. Installation and Setup Complexity
Installation of the web guide system can also affect the decision-making process. Laser-based systems tend to be easier to install with simple setups and minimal calibration. These systems are usually plug-and-play, which makes them perfect for those facilities that need a quick and easy integration. Camera-based systems require a more complex installation. Careful attention is needed to set up the lighting and calibrate image processing software. In environments where rapid implementation is required, this additional setup time may be an issue.
Summary
- The laser-based web guide system is the ideal solution if you need high-speed tracking of simple materials, such as clear film or paper, and also want to want a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution.
- If you work with irregular, complex materials or multi-patterned materials, need more flexibility than simple alignment, such as logos or printed patterns, or you need to inspect multiple characteristics of the web, a camera-based web guide system is the better option.
Final Thoughts
Laser-based and camera-based web guide systems both have unique advantages and limitations. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each web guiding system will help manufacturers make informed decisions to improve web guiding performance and production efficiency.

