The Crucial Role of Web Tension Control in Converting Machinery: Ensuring Precision and Quality in Manufacturing Processes
Web tension control in converting machinery is critical in ensuring the quality and precision of the production process in the realm of converting machinery, where raw materials are turned into final products. Maintaining proper tension in the web (the continuous material being processed) is critical for getting the best outcomes in the creation of flexible packaging, paper, textiles, or other converted products. This article explores the significance of web tension control in converting machinery, challenges of web tension control, and the various methods employed in converting machinery to achieve consistent and high-quality outcomes.

The Importance of Web Tension Control in Converting Machinery
The force applied to the material as it passes through the converting machinery is referred to as web tension. For numerous reasons, proper tension control is critical.
Quality Assurance
Consistent web tension is essential for manufacturing high-quality final products. Irregular tension can cause problems in the completed material such as wrinkles, folds, or misalignments.
Productivity
Precise tension control enhances the efficiency of the converting process. It enables higher production speeds, reduces downtime due to web breaks, and ensures a smoother workflow.
Material Savings
Accurate tension control minimizes material waste by preventing overstretching or sagging of the web. This is particularly important in industries where raw materials are expensive.
Challenges of Web Tension Control in Converting Machinery
1. Variability in Material Properties
Different materials exhibit varying elasticity, thickness, and mechanical properties. Controlling tension becomes challenging when processing a range of materials on the same converting machinery.
2. Speed Changes
Changes in production speed, such as acceleration or deceleration, can lead to fluctuations in tension levels. Rapid speed changes can be especially problematic in maintaining consistent tension.
3. Web Slippage
Inconsistent tension can cause web slippage, which occurs when the material does not move consistently through the converting machinery. This might result in faults and disturbances in the manufacturing process.
4. Roll Diameter Changes
The diameter of the roll changes as it unwinds, affecting tension. Managing tension with different roll diameters can be difficult.
5. Web Splicing
Splicing two webs together might result in abrupt tension shifts. If not properly regulated, this might result in bugs or even web breaks.
6. Environmental Factors
Changes in humidity, temperature, or other external factors can have an impact on material qualities and, as a result, tension control requirements.
7. Mechanical Wear and Tear
Components of converting machinery, such as rollers, bearings, and brakes, may wear and tear over time, impacting their performance and, as a result, tension control.
8. Complex Machine Configurations
Converting machinery with complex configurations, such as multiple unwind and rewind stations, may pose challenges in maintaining uniform tension across the entire process.
Common Methods of Web Tension Control in Converting Machinery
Various methods and systems are employed to control web tension in converting machinery, each offering unique advantages based on the specific requirements of the manufacturing process.
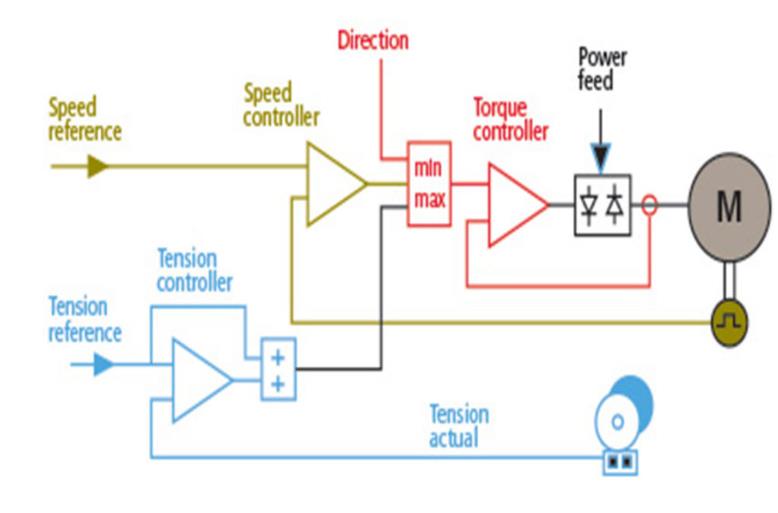
1. Open-Loop Tension Control
Description: In open-loop tension control, operators manually set and adjust tension levels based on their judgment and experience.
Application: This method is suitable for simple processes with minimal tension variations. However, it lacks precision and may result in inconsistencies.
2. Closed-Loop Tension Control
Description: Closed-loop tension control involves the use of feedback systems to continuously monitor and adjust tension levels based on real-time data.
Application: This web tension controller is ideal for processes where precise tension control is required. Sensors placed at strategic points on the machine provide feedback, enabling automated adjustments to maintain optimal tension levels.
3. Dancer Systems
Description: Dancer systems use rollers or arms to accumulate and release web material, creating a buffer that helps absorb tension variations.
Application: Dancer systems are effective for low to moderate tension applications. They provide a mechanical means of controlling tension and are often used in applications where a gentler tension control is required.
4. Load Cells and Tension Sensors
Description: Load cells and tension sensors measure the force applied to the web at various points in the converting machinery.
Application: The data from load cells and sensors are used to adjust the torque or braking force applied by the machine, ensuring consistent tension levels. This method is suitable for processes that demand high precision.
5. Pneumatic and Hydraulic Systems
Description: Pneumatic and hydraulic systems use air pressure or hydraulic force to apply tension to the web.
Application: These systems offer precise tension control and are suitable for high-tension applications. However, they can be more complex and expensive compared to other methods.
6. Motorized Unwind/Rewind Systems
Description: Motorized unwind and rewind systems use motors to control the speed of unwinding and rewinding rolls, thereby controlling tension.
Application: This method is effective for processes with varying material properties. The motorized system adjusts the speed to maintain consistent tension levels.
7. Brakes and Clutches
Description: Brakes and clutches control tension by applying resistance to the material as it moves through the machinery.
Application: These mechanical systems are cost-effective and suitable for applications where precise tension control is not as critical.
8. Tension-Controlled Accumulators
Description: Accumulators accumulate and release material in reaction to tension changes, assisting in the maintenance of a steady flow.
Application: Tension-controlled accumulators are useful in processes where tension variations need to be minimized, such as in the production of sensitive materials.
Conclusion
Web tension control in converting machinery is critical, influencing the production process’s quality, productivity, and efficiency. As technology evolves, the industry continues to look for new ways to overcome obstacles and improve tension control systems. Manufacturers are investing in technology that assure reliable and consistent material processing, ultimately leading to higher-quality final products, ranging from open-loop to closed-loop control and mechanical to electronic systems. Web tension control will be a key topic for optimizing converting machinery processes across numerous industries as the demand for precision in manufacturing develops.

