How Innovations in Printing Inspection Revolutionize Quality Control in Print Industry
In today’s highly competitive printing business, speed, precision and assurance of quality are crucial. As the expectations of customers are increasing and the demands of regulatory demands rise, the printing inspection systems have improved substantially. These advancements not only increase the accuracy and speed of printing inspection but also enable smarter, more interconnected production settings. This article is focused on the most recent innovations in printing inspection and examines the ways they are changing the printing quality control.
Traditional Printing Inspection Methods
| Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
| Visual (Manual) Inspection | Human operators examine the printed material visually for any defects. | – Cost-effective – Flexible judgment | -Human error is a common cause. – Inconsistent -It is not scalable. |
| Magnifying Glass or Loupes | Manual inspection with magnifying tools to find tiny flaws | – Improved visibility of detail | – Slow – Still subjective – Fatigue-sensitive |
| Light Tables | Illuminated surfaces are used to highlight imperfections in prints by looking at prints with backlight | – This is helpful for clarity and registration errors | -Limits to specific materials – Operator-dependent |
| Check Sheets/Manual Logs | Quality checks and defect tracking are recorded manually | – Easy to implement | – Time-consuming It is difficult to evaluate trends |
| Offline Sampling Inspection | Samples from a print run that have been selected tested in a controlled laboratory setting | – A detailed analysis is possible | – Not in real-time. – May miss random/rare defects |
| Comparator Tools | Devices or overlays utilized to evaluate printing samples with master templates. | – Great to check layout and registration | – Limited defect scope – A slower process |

Challenges in Modern Printing Inspection
| Category | Challenge | Description |
| Human Limitations | Inconsistency in Manual Inspection | Human inspectors can miss small imperfections due to fatigue or a lack of objective judgment. |
| High-Speed Production | Limited Inspection Time | Speedy printing speeds make it difficult to identify and respond to any issues in real time. |
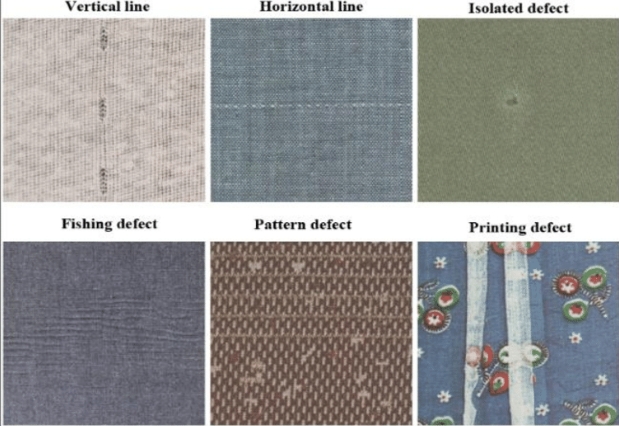
| Defect Diversity | Wide Range of Possible Defects | Smudges, color shifts, misalignment and surface defects require a variety of techniques for detecting them. |
| Complex Substrates | Reflective or Textured Surfaces | Materials such as foil, transparent film or embossed surfaces are hard to examine continuously. |
| Color Accuracy | Subtle Color Variations | The detection of slight color variations is difficult, especially in different lighting conditions. |
| Print Variability | Tolerance in comparison to. True Defect Differentiation | The process of separating acceptable variations from actual defects, without false positives is a challenge. |
| Data Management | Handling and Analyzing Large Volumes of Data | High-resolution images as well as inspection data require a robust system for storage, processing and analysis. |
| Integration Issues | Compatible to Existing Press and Workflow Systems | Inspection systems need to seamlessly integrate with a variety of printing configurations, without disrupting. |
| Cost Constraints | High Initial Investment | Advanced inspection systems can require substantial capital investment as well as regular maintenance. |
| Training and Usability | Operator Skill Requirements | Advanced systems require experienced personnel for calibration, setup and troubleshooting. |

Key Innovations in Printing Inspection
1. AI-Driven Defect Detection
Artificial intelligence is altering the world of inspection. The traditional inspection systems relied on strict rules to detect defects that often led to excessive false rejection rate. The modern AI-powered defect detection systems are able to learn from the data and continually improve, identifying complicated or minor defects with astonishing precision.

The key capabilities are:
- Learning to adapt from the previous inspection results
- Identification of true defects from acceptable variations
- Pattern recognition to avoid repeated mistakes
The classification of the types of defect to aid in better analysis of root causes.
2. Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imaging
Conventional cameras identify flaws visible to the naked eye, but imaging techniques that use hyperspectral or multispectral images enhance inspection capabilities beyond the visible spectrum. They could:
- Find chemical composition changes in the ink or substrate
- Find invisible UV/IR markings for security or traceability
- Resolve surface and sub-surface issues that aren’t visible with standard lighting
These new technologies are particularly beneficial for pharmaceutical packaging as well as security printing and labels for specialty products.
3. Real-Time Edge Processing and Smart Cameras
The modern 100% Print Inspection systems are getting smarter and more efficient with the ability to process images on board. Also known as edge computing, this technique allows for real-time analysis directly from the camera unit, without having to send information via a remote server.
Benefits include:
- Ultra-low latency
- Faster defect response times
- Data transmission loads are reduced.
- Simple integration into high-speed presses
Smart cameras with built-in algorithms are able to immediately reject or flag defective prints, which is ideal for inspection in-line on production lines that are high-speed.

4. Advanced Lighting Solutions
Lighting is crucial for highlighting print defects. New developments with LED technology have brought about:
- Intelligent lighting systems that can adjust the brightness and angle in real-time
- Dark-field lighting and coaxial to improve texture and surface defects detection
- Strobe lighting for freeze-frame image at high speeds
These innovations in lighting ensure constant and glare-free examination even on reflective or glossy materials.
5. 3D Surface Inspection
Flat imaging can be a problem in the inspection of embossed, debossed or tactile elements. 3D surface inspection with laser triangulation, or specially-designed lighting can detect:
- Embossing flaws
- Printing inconsistencies that have been raised
- Perforations and die-cutting mistakes
This is particularly valuable in the areas of luxury packaging and label embossing and for security printing verification.
6. Cloud Integration and Data Analytics
Advanced printing inspection systems are now connected to cloud platforms to monitor remotely data storage, remote monitoring, and analytics. This enables operators to:
- Monitor trends in defect patterns over time or across Machines
- Access inspection results can be accessed from any point
- Integrate the data from inspections in ERP or MES systems.
- Create reports to ensure audits and compliance
Cloud connectivity also facilitates the use of predictive maintenance, which can reduce the chance of unplanned downtime.
7. Seamless Press Integration and Automation
New automated web inspection systems for printing quality are designed to seamlessly integrate to printing presses. By using real-time feedback loops they are able to:
- Stop the press automatically upon finding major flaws
- Trigger alarms, or divert the faulty material
- Change print parameters on the fly based on data from inspections
Automation increases productivity, minimizes the need for manual intervention and reduces the amount of waste material.

Future Trends in Printing Inspection
With the demand for accuracy, customization, and automated is increasing the future of printing inspection is being redefined by new technology and changing production requirements.

1. Integration with Smart Manufacturing
The most well-known trends is the integration printing inspection into manufacturing ecosystems that are smart. Inspection systems won’t work in isolation, but become part of a connected production line. With the Industry 4.0 frameworks the systems will transmit real-time data to other equipment, which will allow for the dynamic adjustment of processes as well as predictive maintenance. complete ability to track quality indicators.
2. AI-Driven Predictive Quality Control
Artificial Intelligence will continue to move beyond defect detection to the area that of more predictive quality controls. Future systems will look at patterns across multiple cycles of production to detect problems before they arise. By analyzing patterns in the behavior of ink as well as substrate variation and environmental variables, AI can help printers make informed decisions that will reduce production time and waste.
3. Adaptive and Self-Calibrating Systems
Inspection equipment for printing is moving towards more autonomy. Future equipment will be able of self-calibration and automatically altering camera settings, brightness and other parameters for inspection in accordance with the job being printed. This flexibility will reduce the time required to set up and will ensure high inspection quality over a broad variety of formats and materials.
4. Sustainability and Waste Reduction
With the increasing emphasis on sustainability, inspection tools will aid in reducing waste by allowing more precise defects tracking and rejection earlier in the process. Future developments will also incorporate more efficient integrated recycling methods as well as eco-friendly materials, enabling more sustainable operations without sacrificing quality control.
5. Augmented Reality for Quality Monitoring
Another trend that is gaining momentum is the application of AR (AR) to improve the interaction of inspectors in conjunction with the inspection system. AR tools offer visual overlays of data about defects along with system status and corrective actions, all in real-time which will help technicians make quicker and more informed decisions right on the press side.
6. Customization and Modular Solutions
As print applications diversify–from flexible packaging to textiles and electronics–inspection systems will be increasingly modular and customizable. Future solutions will be developed to meet the specific needs of each industry and allow printers to expand or enhance functions as they need without having to completely overhaul the entire system.
Summary
The latest innovations in printing inspection are revolutionizing the ways in which print quality can be managed. With AI-enhanced defect detection, smart image processing, advanced lighting and seamless integration, advanced printing inspection system is quicker and more precise than before. As print industry continue to advance, the future of printing inspection is in higher-level intelligence, integration and adaptability and inspection systems are becoming more and more critical in delivering consistent and free of defects, which will ensure the satisfaction of customers and operational excellence.

