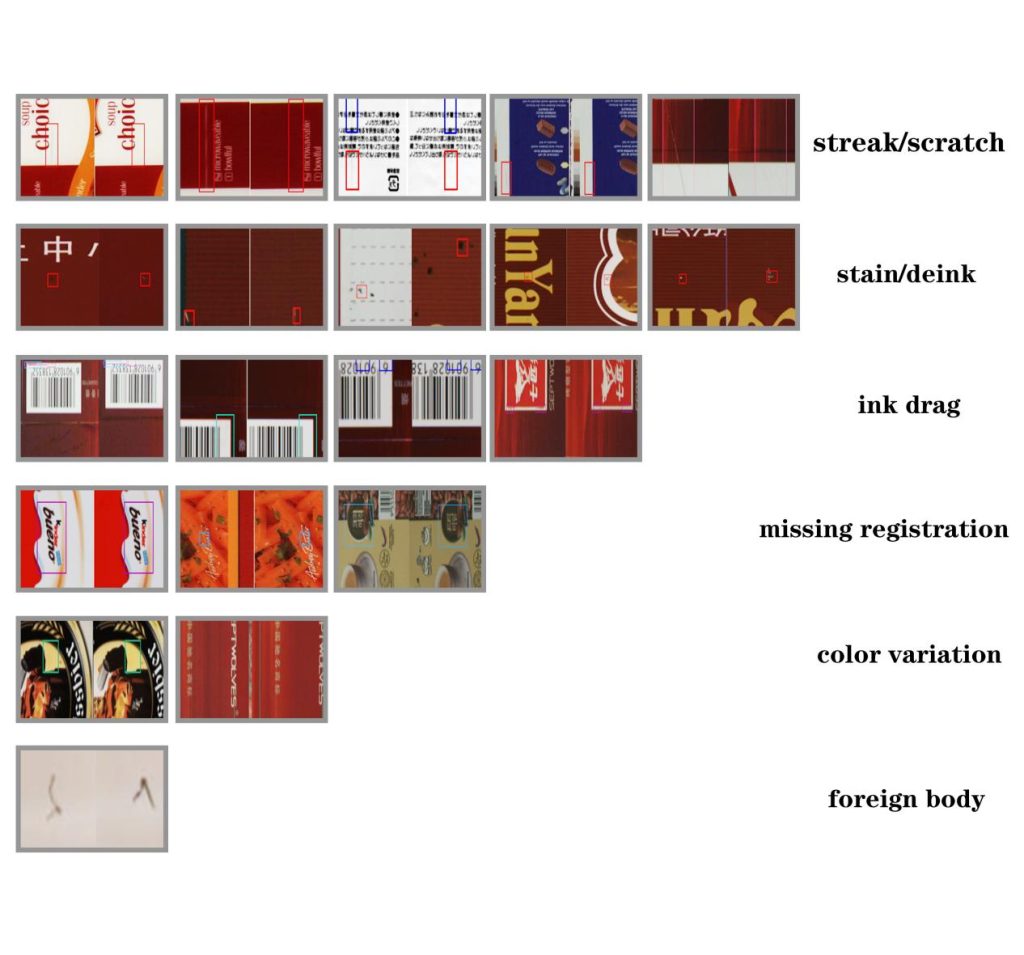
Adaptive Print Inspection for Variable Data
The past few years have seen an increase in demand for personalized and variable data printing in the print industry. Companies are looking for customized printed materials for packaging, direct mail, labels, and tickets. This need for customized print runs, where the content, arrangement, and even the style of each printed piece differs, is highly marketed and operationally flexible, but difficult to execute in high-quality print inspection for consistent quality. One of the greatest challenges in quality control is that traditional print inspection systems are set to review prints against a static master template, and every printed item in the request is expected to differ. This is where adaptive print inspection for variable data becomes necessary to maintain quality and efficiency in production.

Table of Contents
Understanding Variable Data Printing and Its Challenges
Digital printing technologies have made variable data printing more accessible and is a standard practice to allow different text, images, and barcodes (even QR codes) to be printed on each copy within the same printing run. But with the added operational flexibility comes challenges to quality control.

Here’s a chart summarizing the Challenges in Variable Data Printing Inspection
| Challenge | Description | Impact |
| Dynamic Content | Each printed item can contain unique text, images, or codes. | Traditional fixed-template inspection systems cannot effectively verify all variations. |
| High-Speed Production | Printing presses operate at fast speeds. | Manual inspection becomes impractical, increasing the risk of undetected errors. |
| Complex Layouts | Variable designs may include multiple images, graphics, or overlapping elements. | Misregistration, color deviations, and print defects are harder to detect. |
| Accurate Data Verification | Text, numbers, barcodes, and QR codes must match intended values. | Errors can lead to regulatory non-compliance, misprints, and customer dissatisfaction. |
| Color and Material Variations | Different substrates, inks, or coatings may affect print quality. | Ensuring consistency across varying materials is technically challenging. |
| Limited Real-Time Feedback | Errors may not be detected immediately without automated systems. | Delays in correction can result in large volumes of defective prints. |
| Integration Complexity | Inspection systems need to work with multiple file formats and production workflows. | Poor integration can slow production and reduce inspection efficiency. |
Without proper inspection, errors in variable data printing can lead to misprints, legal issues (in regulated industries), wasted materials, and damage to brand reputation.

What is Adaptive Print Inspection
Adaptive print inspection is a quality control technology that has evolved in and now functions within the realm of variable data printing. As opposed to the traditional systems that rely on fixed print templates to be used for comparison, adaptive systems are capable of adjusting the comparison frameworks and criteria dynamically based on the unique elements of each print run as opposed to a fixed control print copy.
- Employ Intelligent Algorithms: Anomalies in texts, images, codes, and graphical elements are detected regardless of the differences in the printed materials. This is possible using machine learning and computer vision.
- Deliver Feedback Instantly: Where every expected quality is deviated, say a misaligned text, a smudged barcode, or wrong information, the system will issue a direct command in order to correct the mistake.
Such an approach allows the operators of the printed item to carry out the job without shoting for accuracy and constance from whichever a large number is to be eliminated stationary templates.
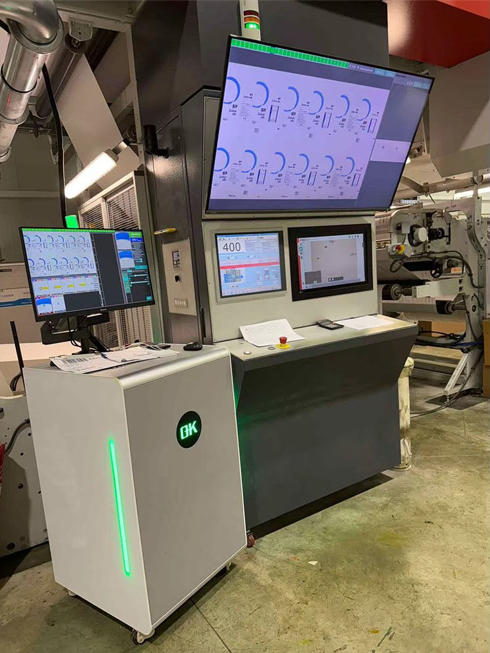

Key Components of an Adaptive Print Inspection System
| Component | Function | Role in Variable Data Inspection |
| High-Resolution Cameras | Capture detailed images of each printed item | Enables detection of fine defects, misalignments, and print inconsistencies in real time |
| Optical Character Recognition (OCR) | Reads and verifies text and numeric data | Ensures variable text matches the intended print file accurately |
| Barcode and QR Code Verification | Scans and validates codes | Confirms codes are correct, readable, and properly positioned on each item |
| Image and Color Analysis | Evaluates images, graphics, and color consistency | Detects misregistration, color deviations, or image defects even with dynamic content |
| AI and Machine Learning Models | Analyzes print patterns and learns over time | Improves detection accuracy and adapts to variations in design or layout |
| Real-Time Feedback Systems | Alerts operators instantly about defects | Allows immediate correction to prevent large-scale errors and material waste |
| Data Analytics and Reporting | Tracks defects, trends, and process performance | Provides insights for process optimization and quality improvement |

The Step-by-Step Working Process of Adaptive Print Inspection System
Knowing the stepwise function of these print inspection systems enables the operators to maximize quality, reduce inconsistency and waste, and achieve a steady output.
Step 1. Pre-Print Data Preparation
Digital print files are deployed and the system comes with a layout to be used that includes images, texts with variables, barcodes, and graphics to be integrated. Then, the production specifications are integrated into the layout and the inspection parameters are set. Variations expected in each print job will inform the system in differentiating the differences that are ok from the misalignments that are to be gaps in the job.
Step 2. High-Resolution Image Capture
High resolution cameras are initiated while printing to record every detail for each printed item. These cameras are set to capture every possible angle while every printed item is produced. The images taken are the basis for all the subsequent inspection. Since each printed variable data piece contains unique content, the documentation error capture, as well as the documentation of every piece is of utmost importance for error detection.
Step 3. Image Processing and Alignment
Each captured image is processed to align every printed material with the digital record. The system accounts for adjustments in position, rotation, or distortion during high-speed printing. To avoid variations in position or orientation from triggering false positives, images are standardized, so the system is balanced. Alignment is critical in variable data printing. Small levels of misregistration can drastically impact text legibility or barcode scanability.
Step 4. Optical Character Recognition and Data Verification
The following procedure integrates the use of optical character recognition (OCR) and data extraction from the hard copies of documents. In this case, it is the verification of variable content such as names, serial numbers, and expiration dates against the targeted digital file. Data-verification processes flag missing or extra characters and incorrect numbers, all of which require immediate attention. This process is crucial for the direct mail, packaging, and security printing industries. In these industries, the accuracy of variable data is indispensable.
Step 5. Barcode and QR Code Analysis
In the case of documents which includes bar codes, or QR codes, the system initiates a confirmatory procedure to determine whether or not these codes are valid, legible, and correctly aligned within the document. The inspection system is smart enough to identify wrong codes, as well as any condition that may render the codes inactive, such as smudging or misalignment. This procedure is highly significant for the management of supply chains, the pharmaceutical industry, and ticketing for events as it is highly disruptive to operational processes and regulatory compliance to have defective codes.
Step 6. Image and Color Inspection
In addition to evaluating texts and codes, the system reviews the images, graphics, and colors for uniformity and quality. Sophisticated algorithms analyze printed visuals relative to what they should be and identify flaws including text and images that are misplaced, blurred, color differentiated, or otherwise misaligned. Adaptive inspection systems can accommodate and identify errors in systems that feature dynamic layouts, in which each printed piece contains differing images or designs.
Step 7. Real-Time Feedback and Error Handling
The ability to deliver feedback instantly stands out as the most remarkable feature of adaptive print inspection systems. When a defect occurs, these systems flag it instantly, giving operators the chance to make corrections before excessive waste occurs. Some systems are designed to automatically halt the press or eject defective components from the line to guarantee only pristine prints are forwarded to subsequent processing. This type of error response optimizes the system, preserves the material, and protects the integrity of the business.
Step 8. Data Logging and Analytics
All inspection results are logged and analyzed. Comprehensive reports contain records of gaps and trends pertaining to errors, including their types, locations, and frequencies. From these records, great insights into optimizing processes are gathered. Returning to these analyses, print operators are competent in diagnosing problems and adjusting inspection controls to improving production quality in successive iterations. While still in the early stages, the system learns to align adaptive print inspection to variable new designs as a means of decreasing errors of commission.

Key Advantages of Using Adaptive Print Inspection for Variable Data
1. Enhanced Accuracy for Personalized Content
The verification of printed adaptive inspection is unmatched. Unlike older systems which depend on inspection templates, adaptive systems are capable of adjusting to a variety of text, images, and codes. Therefore, every item, irrespective of whether it is personalized with a name, an address, or any graphic, will be exactly as intended without any faults.
2. Reduction of Waste and Material Loss
When errors are made in variable data printing, it is easy to lose a lot of materials. Immediately after an adaptive inspection system identifies a defect, the operator is able to make adjustments. This minimizes the number of misprints, and in turn, the amount of wasted paper, labels, ink, and production costs, which in turn, improves the sustainability of the printing process.
3. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Numerous industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and security printing, require compliance with labeling and identification standards. Adaptive print inspection affirms that variable information, including batch, expiration, and security codes, are checked for accuracy and readability. As compliance is maintained automatically, companies are spared fines, recalls, and reputational losses.
4. Increased Production Efficiency
Turning to adaptive outside and adaptive in-line systems for real-time inspection and print quality evaluation affords unimpeded productivity. Severe unimpeded automation of quality control without slowing down the front of the production line is possible. The operators focus on other tasks of the production process control. Quality is sustained on every single printed piece or imprinted item.
5. Real-Time Error Detection and Correction
Adaptive systems’ greatest advantage is real-time defect detection. In the instance of quality control failing, operators are told and some systems go as far as auto removing or stopping flow of defective pieces. Systems’ on-the-spot control systems guarantee that faulty prints are kept to a minimum on the flow and only quality assured products get to the consumer.
6. Data-Driven Insights for Process Improvement
Adaptive print inspection systems outline extensive print inspection analytics that document pattern errors, identify trends, and assess production performance. Such assessments assist operators in discerning persistent problems and refining parameters for effective printing. Over time, natural language processing algorithms will enhance the systems, and the redundancy of problems will decrease, improving overall workflow.

Applications across Industries of Adaptive Print Inspection for Variable Data
| Industry | Application | Importance of Adaptive Inspection |
| Direct Mail and Marketing | Personalized mailers, promotional materials | Ensures correct names, addresses, and messages on every piece, maintaining campaign effectiveness and customer trust |
| Packaging and Labels | Product labels, expiration dates, batch numbers | Verifies variable codes and text to prevent regulatory non-compliance and consumer confusion |
| Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare | Prescription labels, medical records, sample packaging | Guarantees accuracy of patient information, dosage, and regulatory details to ensure safety and compliance |
| Security Printing | Tickets, vouchers, certificates, ID cards | Detects misprints, duplicates, or incorrect serial numbers to prevent fraud and maintain security |
| Retail and E-commerce | Price tags, loyalty cards, shipping labels | Confirms correct pricing, codes, and barcodes for operational efficiency and customer satisfaction |
| Event Management | Customized passes, tickets, wristbands | Ensures that variable information such as seat numbers or access levels is correct and scannable |
| Food and Beverage | Nutritional information, barcodes, lot codes | Maintains compliance with labeling standards and prevents mislabeling that could harm consumers |
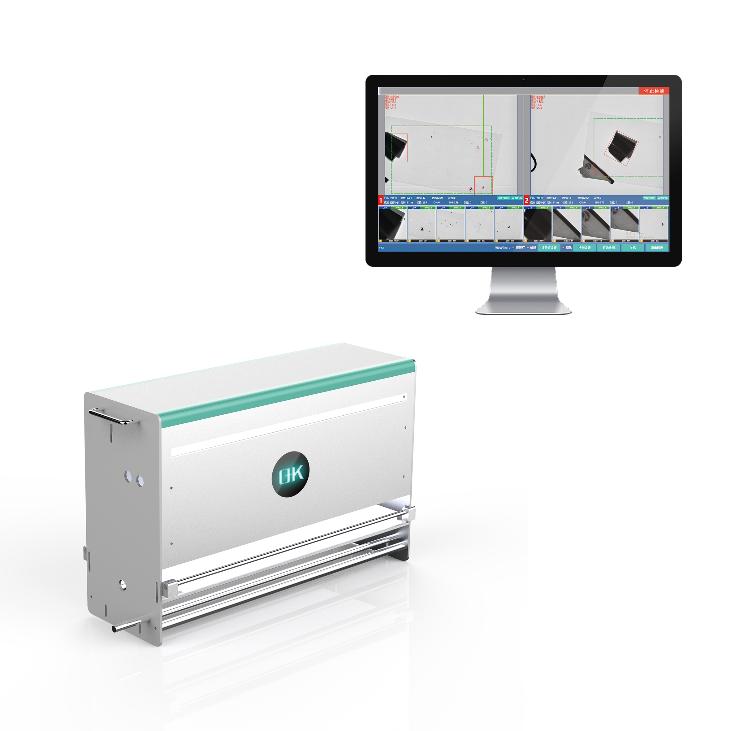

Future Trends in Adaptive Print Inspection System for Variable Data
Among the most rapidly evolving adaptive print inspection, is the 100% print inspection system. As adaptive print inspection systems follow the developments in printing technologies and the burgeoning need for personalized variable data, print inspection systems themselves become more intelligent, rapid, and integrated, enabling print processes to meet production challenges with an emphasis on accuracy and efficiency. This illustrates the direction adaptive print inspection systems will pursue to meet the remainder of the variable data printing needs.
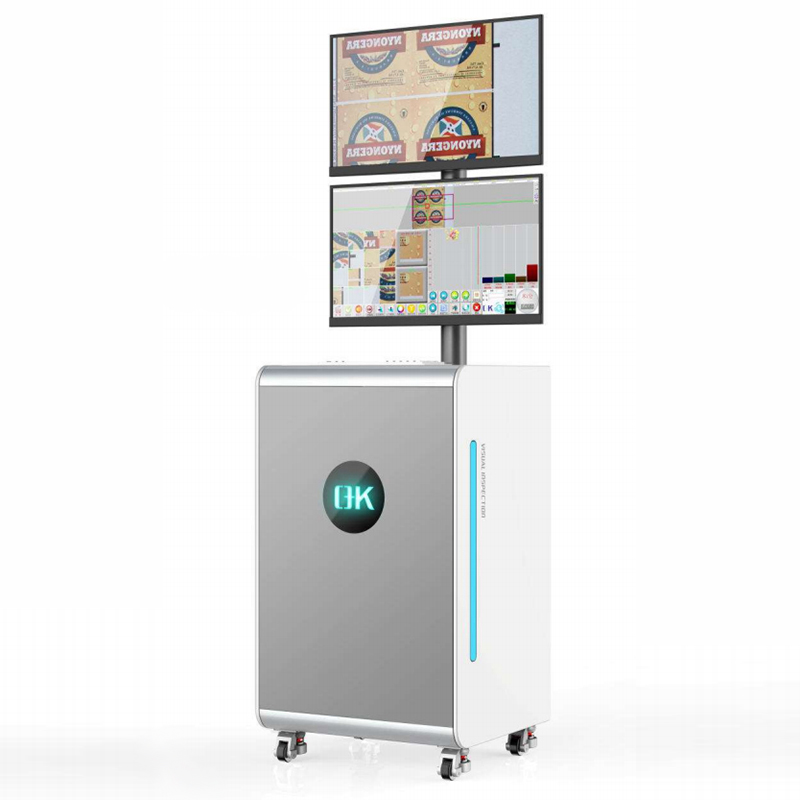

1. Real-Time Analytics and Cloud Connectivity
Future adaptive inspection systems will integrate with cloud technologies in real time for centralized monitoring and tracking. Linking multiple printing centers to one cloud infrastructure allows businesses to manage production quality for multiple locations, monitor defect trends, and access information. This integration allows for remote system updates, troubleshooting, and streamlined systems which ultimately minimize downtime.
2. Advanced Image Recognition and Color Analysis
With the complexity of variable data printing increasing, every inspection system will have to depend more on advanced image recognition and advanced color analysis. This technology permits the system to identify even the smallest divergences in intricate graphics, images, and brand colors. Enhanced algorithms will also improve the inspection of new materials, substrates, and contemporary techniques of printing, regardless of the complexity of the design, to provide quality control.
3. Enhanced Barcode and QR Code Verification
Given the ubiquity of barcodes and QR codes, as well as other scannable tokens in logistics, healthcare, and packaging, we will see advanced inspection systems deliver more sophisticated verification systems. These systems will rapidly decode, identify and mitigate errors in difficult situations, and cross-reference to provide error-proofing and traceability.
4. Automation and Robotics Integration
Emerging trends also include the integration of automated printing lines and robotics with adaptive inspection systems. Automation of defect detection will lessen human structural intervention and increase the speed of production. The incorporation of inspection technology with automation will allow printing operations to perform quality control seamlessly and to a full circle in the process. This will result in maximum efficiency and minimal material waste.

5. Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Sustainability will certainly be an enduring focus across the printing industry. Adaptive print inspection systems help with this by minimizing waste through early defect detection and efficient print run optimization. Future advancements will perhaps focus on more precise tracking and control of ink and substrate balances and energy expenditures, thereby allowing firms to integrate environment-driven quality control with core print run parameters.
6. Customizable and Scalable Systems
Increased diversification of print operations will result in adaptive inspection systems becoming increasingly modular and scalable. Organizations will be able to customize print inspection parameters, attach new verification systems, and expand the functionality of the systems to fit their production requirements. This scalability guarantees that organizations will have the flexibility to handle numerous variable data printing projects and protect print quality.

Summary
Adaptive print inspection for variable data is essential for personalization, precision, and efficiency modern printing operations demand. An Automated web inspection system during printing operations, empower companies to deliver high-quality work during even the most volatile printing processes, thereby allowing them to minimize waste and preserve quality. 100% inspection systems will be pivotal in quality control as variable data printing expands, enabling companies to produce dependable, precise, and powerful printing products.

